cluster sampling in quantitative research|is a cluster sample probability : solutions Cluster sampling (also known as one-stage cluster sampling) is a technique in which clusters of participants representing the population are identified and included in the sample. This is a popular method in conducting marketing . web19 linhas · Siga tudo sobre Campeonato Português. Notícias, classificação, estatísticas e mais na ESPN.
{plog:ftitle_list}
The latest tweets from @ponstar_KTR
Cluster sampling (also known as one-stage cluster sampling) is a technique in which clusters of participants representing the population are identified and included in the sample. This is a popular method in conducting marketing .
Cluster sampling, a versatile approach in statistical or survey research, can be implemented in various forms depending on the research objectives and constraints. The two primary types are single-stage and multistage cluster . Cluster sampling is a statistical sampling method used in research studies where the population is large and geographically dispersed. The cluster sampling method involves . Cluster sampling allows researchers to create smaller, more manageable subsections of the population with similar characteristics. Cluster sampling is particularly useful in areas of geographical sampling when the . Cluster sampling has several advantages compared to other methods of data collection. These include: Cost-effective – It requires minimal resources and personnel to carry out the sampling process, making it a highly cost-effective method.. Accuracy – Cluster samples can provide a more accurate reflection of a population of interest than other methods, given .
A cluster sample is a sampling method where the researcher divides the entire population into separate groups, or clusters. Then, a random sample of these clusters is selected. All observations within the chosen . Cluster sampling is the process of dividing the target population into groups, called clusters. A randomly selected subsection of these groups then forms your sample. Cluster sampling is an efficient approach when you want to study large, geographically dispersed populations. . Probability sampling. In quantitative research, it is important .
why is cluster sampling good
The research used quantitative methodology and relied on two data acquisition techniques. . stratified sampling, cluster sampling and disproportional sampling. Nonprobability sampling includes .Chapter 8: Quantitative Sampling I. Introduction to Sampling . Cluster sampling addresses two problems: Researchers lack a . (RDD) is a special sampling technique used in research projects in which the general public is interviewed by telephone. Here is how RDD works in the United States. Telephone numbers have three parts: a three-digit .What is Cluster Sampling? Cluster sampling is a probability sampling technique where researchers divide the population into multiple groups (clusters) for research. So, researchers then select random groups with a simple random or systematic random sampling technique for data collection and unit of analysis.. Example: A researcher wants to conduct a study to judge .
3.4 Sampling Techniques in Quantitative Research Target Population. The target population includes the people the researcher is interested in conducting the research and generalizing the findings on. 40 For example, if certain researchers are interested in vaccine-preventable diseases in children five years and younger in Australia. The target population will be all children aged . Cluster Sampling in Market Research; In market research, cluster sampling allows organizations to collect relevant responses from a vast target audience spread across multiple geographical locations. When creating market research surveys for geographical areas, it can get pretty expensive and time-consuming to attempt to survey a broad region. . The research sample was selected through cluster random sampling technique. The cluster random sampling technique is used when there is no sampling frame (list of names of all members), and the . When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the .
Cluster Sampling: In this method, the population is divided into clusters or groups, and then a random sample of clusters is selected. Then, all members of the selected clusters are included in the sample. . The data collected is quantitative and statistical analyses are used to draw conclusions. Purpose of Sampling Methods. The main purpose .
Cluster sampling . According to Taherdoost (2016), the normal or appropriate sample size for quantitative research studies is 40% of the participants. Therefore, this study's response rate was . Also called judgmental sampling, this sampling method relies on the researcher’s judgment when identifying and selecting the individuals, cases, or events that can provide the best information to achieve the study’s objectives. Purposive sampling is common in qualitative research and mixed methods research.10.3 Sampling in quantitative research Learning Objectives. Describe how probability sampling differs from nonprobability sampling; . Cluster sampling occurs when a researcher begins by sampling groups (or clusters) of population elements . Probability sampling is used in quantitative research, so it provides data on the survey topic in terms of numbers. Probability relates to mathematics, hence the name ‘quantitative research’. Subjects are asked questions like: . This is a more refined way of doing cluster sampling. Let’s say you have your urban cluster, which is your .
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques.Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research, especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings. . With cluster sampling, .
Cluster sampling is a sampling method in which the entire population is divided into externally, homogeneous but internally, heterogeneous groups. . Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more. Discover Full-Immersion Membership.Purposive sampling (also known as judgment, selective or subjective sampling) is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study. Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method and it occurs when . Stratified Sampling | Definition, Guide & Examples. Published on September 18, 2020 by Lauren Thomas.Revised on June 22, 2023. In a stratified sample, researchers divide a population into homogeneous subpopulations called strata (the plural of stratum) based on specific characteristics (e.g., race, gender identity, location, etc.).SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
The research employed a pre-experimental research design, with a one-group pre-test and post-test approach, utilizing a sample of 30 IX C students selected through cluster random sampling methodology.
In cluster sampling, various segments of a population are . . The research utilized a quantitative-correlation design involving 1,494 respondents selected through simple random sampling. Data . What Is Snowball Sampling? | Definition & Examples. Published on August 17, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method where new units are recruited by other units to form part of the sample.Snowball sampling can be a useful way to conduct research about people with .
Non-probability sampling is a sampling method that uses non-random criteria like the availability, geographical proximity, or expert knowledge of the individuals you want to research in order to answer a research question. Non-probability sampling is used when the population parameters are either unknown or not possible to individually identify. When To Use Convenience Sampling. Convenience sampling can be useful in specific circumstances: Preliminary or Exploratory Research: Convenience sampling can be a good starting point when conducting initial or exploratory studies.It allows you to gather preliminary data and insights quickly and efficiently, which can be useful in informing more .
Convenience sampling is a type of sampling where the first available primary data source will be used for the research without additional requirements. In other words, this sampling method involves getting participants wherever you can find them and typically wherever is convenient.
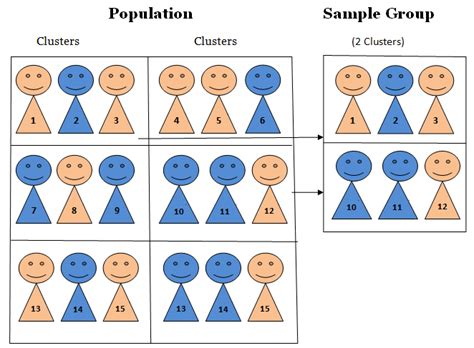
is a cluster sample probability
Read YOVE - Chapter 1 | ManhuaScan. The next chapter, Chapter 2 is also available here. Come and enjoy! A talented art student, a drama queen who gets a kick out of spending on what she likes, befriends an outgoing young model who lives a thrifty life. They grow to appreciate and learn from each other, progressing along the way.
cluster sampling in quantitative research|is a cluster sample probability